Selectivity in size exclusion chromatography (SEC): it’s much more than average pore diameter (Å)
Describing the pore of a size exclusion chromatography resin with a single number such as average pore diameter is an oversimplification. The formation of pores is dependent on complex combinations of many parameters.
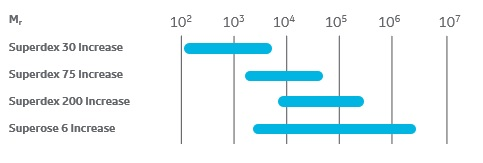
SEC resin fractionation range and selectivity
Selectivity is a measure of the relative retention of two solutes in a column related to the distance between two peaks in a chromatogram. The fractionation range/molecular weight range depends on the pore size distribution of the resin and specifies the range of molecular weights that have partial access to the pores of the resin. This means that molecules within this range should be separable.
The exclusion limit for a SEC resin specifies the size of the molecules that are too big to enter the pores and are therefore eluted in the void volume.
Graph showing the separation ranges of some of Cytiva´s SEC resins for protein analysis
Pore size is about more than average pore diameter
The formation of pores is dependent on complex combinations of many parameters: the pore diameter, the pore shape, the number of pores, and pore connectivity. All pores are not identical within a single resin particle. The selectivity of a SEC resin is determined by the interaction of all of these properties. By modifying resin pore properties, today’s SEC resins can separate biomolecules over a molecular weight range from 100 to 80 000 000 Mr (relative molecular weight), from peptides to very large proteins and protein complexes.
Parameters that affect resolution
Selectivity of a SEC resin indicates the distance between two peaks and depends on the properties of the resin (such as pore size distribution), the interactions between sample and resin, and the conditions used. The selectivity of the resin together with the efficiency, which depends mainly on the particle size, the column format and the packing of the column, affects the resolution between peaks.
To obtain a high resolution (narrow peaks) particle size, column dimension and the packing of the column are all of high importance. Additionally, minimizing system volumes in the chromatography system is important to obtaining a high resolution.
Analytical SEC columns from Cytiva.
Cytiva offers new-generation SEC columns for small-scale preparative purification and analytical size exclusion chromatography.
- Peptides
- Oligosaccharides
- Separation of polyphenols (TCM*)
- Other small biomolecules
- Proteins, enzymes, tagged proteins
- Polysaccharides
- Separation of polyphenols (TCM)
- mAb and other antibodies
- Proteins, enzymes, tagged proteins
- Polysaccharides
TCM = Traditional Chinese Medicine
* The image is reproduced from Wikimedia Commons (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Protein_AP2A1_PDB_1gw5.png) and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.