Purifying histidine (his)-tagged proteins may sound easy. However, there are tips to ensure that you get the most from your his-tagged protein purification protocol, by choosing the right combination of chromatography techniques in a multistep approach.
His-tagged protein purification—it’s all about the balance between protein purity and yield.
The vast majority of proteins purified in research are affinity-tagged and can therefore be purified with relative ease using different types of affinity chromatography (AC) depending on tag that is used. This article focuses on his-tagged proteins, which can be purified by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC).
Sometimes, after the IMAC step, the purity level of his-tagged protein is “good enough” to move forward in the research experiment. However, if the goal is to obtain the highest possible protein purity, a multistep purification protocol may be needed.
- The types of chromatography technique(s) used in the his-tagged protein purification protocol depend on the purity requirement and yield of your protein of interest (Fig 1). The required protein purity level will depend on your application, as shown in the table below.
- Before you start, carefully define your objectives and consider that in general, every added purification step will increase purity but decrease total protein recovery1 and yield2.
1 Recovery = The relative amount of target protein (%) that is retrieved after purification compared with amount loaded on the column.
2 Yield = Amount of target protein obtained after a purification step, or after the entire purification (multiple steps).
| Typical applications | Purity level |
|---|---|
| Mass spectrometry Antigen for immunization |
Moderate, > 80% |
| Functional studies Structural studies |
Very high, 95% to 99% |
| Structural studies Therapeutic proteins |
Highest, > 99% |
How to combine chromatography techniques to set-up a powerful his-tagged protein purification protocol
Figure 1 describes three typical proven technique combinations for purification of his-tagged proteins.
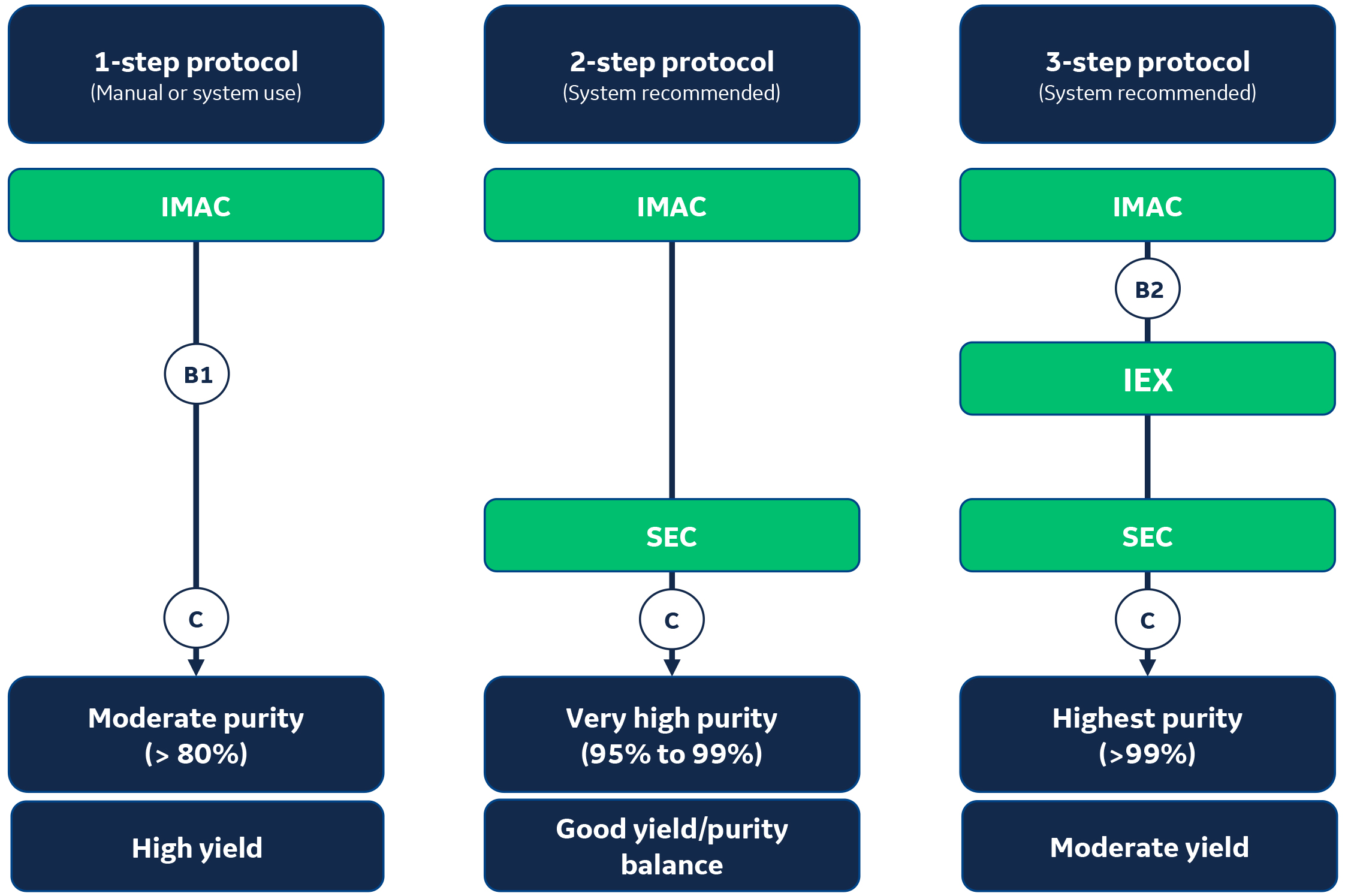
Fig 1. 1-,2-, or 3-step protocols may be deployed to purify his-tagged proteins depending on the goal of the purification (yield vs purity). IEX = ion exchange chromatography; IMAC = immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography; SEC = size exclusion chromatography; B1 = buffer exchange to remove imidazole or salts; B2 = buffer exchange to prepare for IEX; C = concentration for sample volume reduction, which may also be performed before SEC. Steps in circles are optional and are applied if necessary.
It all starts with a first IMAC step
All his-tagged protein purification protocols typically start with an AC (IMAC) step. It enables the isolation of the target his-tagged protein from initial sample (e.g, lysate, cell culture)
After the first AC step run on an IMAC column, the purity level is usually moderate (> 80%).
2-step purification protocol: IMAC + SEC
For applications such as functional studies, a moderate purity level is not sufficient. This is why a size exclusion chromatography (SEC)3 step should be added to remove remaining impurities. The purity level after a 2-step purification protocol will be very high (95% to 99%).
3 Also called “gel filtration”
3-step purification protocol: IMAC + IEX + SEC
In some instances, host cell proteins (HCP) with same molecular weight are co-purified with the his-tagged protein of interest during the IMAC step. In this case, the recommendation is to add an IEX (ion exchange chromatography) step between the IMAC and the SEC steps. The purity level can then increase to higher than 99%, which is essential for protein structural studies.
Importance of buffer exchange and concentration in the his-tagged protein purification protocol
To make the sample compatible with the following steps or experiments, a desalting column (also called a buffer exchange column) is used to exchange buffer between chromatography steps. Furthermore, a concentration unit may also be used to reduce the sample volume if needed.
The following key buffer exchange/sample concentration steps are represented by B and C in Figure 1:
- B1: Buffer exchange to remove imidazole or salts.
- B2: Buffer exchange to prepare for IEX.
- C: Concentration for sample volume reduction. May also be performed before SEC.
Which chromatography columns are recommended for each protein purification step?
Click on the blue buttons in Figure 1 to get column recommendations for each step of the his-tagged protein purification protocol. The buttons also highlight recommended chromatography systems for the three protein purification scenarios.
Automate your multistep purification protocols
If you’re using an ÄKTA pure system or an ÄKTA avant system, you can set up your chromatography system to run multiple chromatography steps automatically.
Purifying other types of proteins?
Read how to combine chromatography techniques to purify antibodies or untagged proteins.