The extraction, isolation and purification of DNA, RNA or total nucleic acids from samples is a critical part of many applications.
Researchers may perform genomic DNA (gDNA) extraction in order to separate the gDNA from the rest of the cellular contents. The advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) techniques has enabled collection of unprecedented amounts of sequencing data in short spans of time. This has greatly contributed to our understanding of genomic and gene structure across many species and has also allowed us to gain much information about candidate genes for genetic disorders, cancer-causing somatic mutations, and misexpression due to epigenetic changes.
Plasmid DNA (pDNA) may be used to express recombinant proteins in various host organisms during molecular biology and protein research.
Total RNA analysis performed using the RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) technique allows researchers to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample at a given moment, analyzing the continuously changing cellular transcriptome. The comparison of transcriptomes of different types of cells can help researchers gain a better insight on the normal functionality of a cell and how gene activity may impact or contribute to disease.
As the throughput in nucleic acid research has increased dramatically, efficient purification of pDNA and gDNA, and RNA isolation in multi-well plates has become a crucial need. To address the needs of researchers working in these areas Cytiva offers a multi-well nucleic acid binding plate.
The AcroPrep™ Advance 96-well Long Tip Filter Plate for Nucleic Acid Binding (NAB plate, a Pall™ Life Sciences product) incorporates a silica-based quartz glass fiber media to allow for efficient binding of DNA and RNA, while providing smooth flow and rapid processing of samples. This media offers researchers the flexibility to purify pDNA from bacteria, and gDNA or total RNA from samples; a single plate is suitable multiple applications.
AcroPrep™ Advance 96-well Long Tip Filter Plate for Nucleic Acid Binding.
The filter plate features long outlet tips, which minimizes hanging drop formation, thus reducing the possibility of cross-contamination when removing the filter plate from the receiver plate post-filtration.
To save researchers cost, NAB plates can be used with commercially available reagents that can be purchased from different manufacturers.
Manufactured in accordance with specifications for the Society of Biomolecular Screening (ANSI/SBS x-2004) for multi-well plates, NAB plates allow for the entire DNA purification process to be performed on automated equipment.
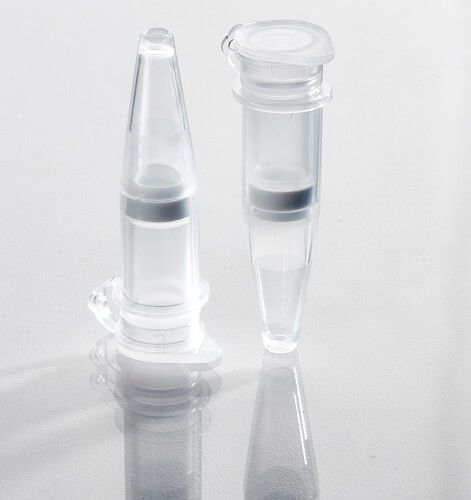
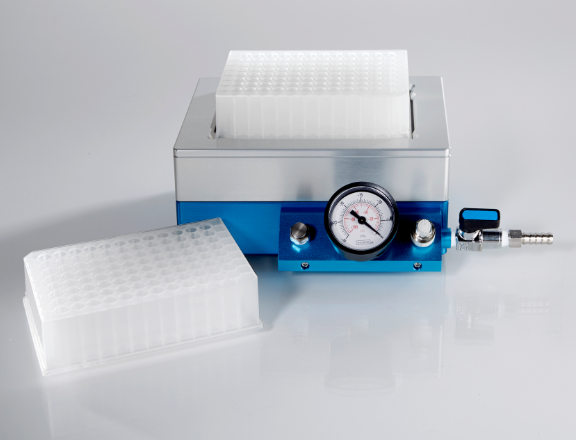
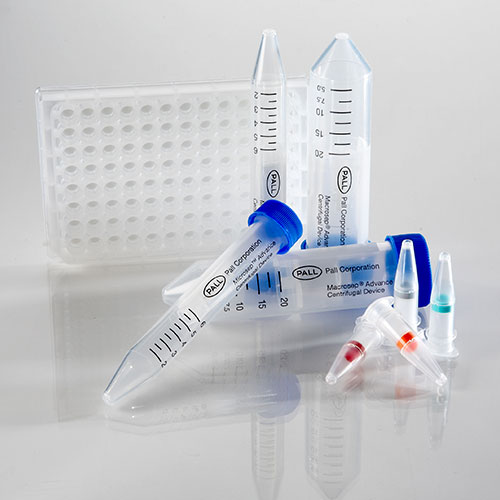
For rapid single-sample processing we offer the Nucleic Acid Binding Nanosep™ Centrifugal Devices (Pall™ Life Sciences products). These spin devices incorporate the same dual layer silica-based quartz glass fiber media as our NAB plates to allow for efficient binding of nucleic acids. Nanosep devices fit in standard centrifuge rotors that accept 1.5 mL tubes and can process samples up to 500 µL in volume.
Nucleic Acid Binding Nanosep™ Centrifugal Devices
Chromatography and ultrafiltration
Additional methods of nucleic acid purification may include chromatography and ultrafiltration steps.
Our AcroPrep™ filter plates (Pall™ Life Sciences products) can be combined with resins to form high-throughput chromatography platforms by simply introducing a chromatography resin slurry into the individual wells of a plate. The filter plates feature a smooth internal well design that allows for uniform resin packing and flow rates across the plate, and the filter plate media forms a platform for the resin. The outlet tip design of the filter plates minimizes sample leakage and loss that could occur during incubation steps.
Alternatively, when performing ion exchange chromatography we offer an innovative chromatography membrane, which can provide higher dynamic binding capacity compared with traditional resin-based solutions. Our Mustang™ chromatography AcroPrep™ filter plates facilitate the removal of host cell proteins, and work to purify gDNA or pDNA. They are easy to use and disposable, creating an optimally sterile environment for purification using ion exchange chromatography.
Ultrafiltration is a membrane separation technique used to separate extremely small particles and dissolved molecules in fluids. The primary basis for separation is molecular size, although other factors such as molecule shape and charge can also play a role. Molecules larger than the membrane pores will be retained, but not bound, at the surface of the membrane and concentrated during the ultrafiltration process.
The retention properties of ultrafiltration membranes are expressed as molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) and measured in kilodaltons (kDa). This value refers to the approximate molecular weight of a dilute globular solute (i.e., a typical protein) that is 90% retained by the membrane. However, a molecule’s shape can have a direct effect on its retention by a membrane. For example, linear molecules like DNA may find their way through pores that will retain a globular species of the same molecular weight.
Cytiva offers ultrafiltration devices with a range of MWCO membranes. Our devices are available in multi-well filter plate formats or as centrifugal filters. The products feature the Omega™ (modified polyethersulfone) ultrafiltration membrane. The low binding nature of Omega ultrafiltration membrane offers numerous benefits, including high recoveries of low concentrations of biomolecules and low surface fouling when performing ultrafiltration applications.
Cytiva ultrafiltration devices
Plasmid DNA
pDNA plays a pivotal role in molecular biology research, but obtaining it from prokaryotic cultures can be tricky. It needs to be separated from genomic DNA in a complex lysis and purification procedure.
pDNA may be used to express recombinant proteins in various host organisms during molecular biology and protein research, and progress in cloning technology has led to the need for numerous samples of small cultures of pDNA. Small-scale preparation of pDNA requires parallel purifications using semi-automated or fully automated handling.
Lysing is the first step in purifying plasmids from within the cultured cells. Once the DNA has successfully been extracted, it must be clarified in order to remove cellular debris. Cytiva supplies 96-well filter plates for cell lysate clearance; our filter plates are available in 350 μL, 1 mL, and 2 mL well volumes. These filter plates contain a 3.0 μm glass fiber depth filter layered on top of a Supor™ 0.2 μm membrane. The 3.0 μm glass fiber acts as a prefilter removing larger particulate contamination and allowing for the efficient usage of the final 0.2 μm Supor membrane filter.