FAQ
How can I check the functionality of my column?
Leading and tailing peaks as defined according to the following figures:


| Leading peak | Tailing peak |
Experience shows that the best method of expressing the efficiency of a packed column is in terms of its height equivalent to a theoretical plate (HETP), reduced plate number (h) and its peak asymmetry factor (As).
Please be aware of that for small columns, less than 10 ml bed volume, the system dead volume has an impact on the column evaluation values.
My column is clogged and/or discoloured. How can I clean my packed column?
Prepacked columns
Please clean the column according to instructions.
Other columns
Please follow the recommendations in the media instructions.
If the issue persists after cleaning you have to replace the column with a new one (prepacked columns) or repack the column with fresh medium.
How would I get the best resolution of my column?
For stand alone columns please assemble the monitor to the column outlet.
If the column is connected to a system, connect the column as close as possible to the monitor.
How do I store my column?
Prepacked columns
Please store the column according to instructions.
Other columns
Please follow the recommendations in the media instructions.
What is the pressure limit of my column?
Prepacked Columns
Please read
Prepacked chromatography columns for ÄKTAdesign systems
Other Columns
| Column |
Maximum pressure (bar)
|
| C 10, C 16 and C 26 |
1
|
| FineLINE Pilot 35 |
20
|
| HiScale |
20
|
| HR (High Resolution) 16 |
30
|
| SR 25 |
1
|
| Tricorn 5 |
100
|
| Tricorn 10 |
50
|
| XK 16 and XK 26 |
5
|
| XK 50 |
3
|
My column is leaking buffer, what shall I do?
Leakage around connectors
| Possible causes | Suggested Remedy |
| Connectors not compatible with each other. | Check compatibility. |
| Connectors not compatible with solvents. | Check chemical resistance with the connector supplier. |
| Connectors poorly positioned or not tightened. | Check the connectors. |
| Gaskets worn out. | Gaskets lose flexibility with time and need to be replaced regularly. Inspect and replace if necessary and at least annually. |
Leaking tubing
| Possible causes | Suggested Remedy |
| Tubing not compatible with solvents. |
Check chemical resistance with the tubing supplier. Preventive action: Always check tubing solvent compatibility prior to packing or running the column. |
Leakage around end-pieces ( Not applicable for the pre-packed columns )
| Possible causes | Suggested Remedy |
| End-piece and O-rings not properly positioned with respect to the tube. | Disassemble the column and check the position of the end-piece and O-rings. Assemble the column according to instructions and perform leakage tests. |
| O-rings worn out | O-rings loose their flexibility with time and need to be replaced regularly. Disassemble the column and inspect the O-rings. Replace if necessary and at least annually. Assemble the column according to instructions and test for leakage. Preventive action: Replace O-rings when needed or at least annually. |
The backpressure increases during operation
| Possible causes | Suggested Remedy |
| Auxiliary equipment such as manometers and pumps not working properly. | Check the function of all auxiliary equipment. Repair/replace if necessary. |
| Column is clogged. | Clean the column according to instructions. Choose the more rigorous cleaning protocol when available. See media and column instructions. |
| Bent tubing. | Check that the flow path is not restricted. |
| Buffer viscosity too high. | Check the viscosity of all buffers. Viscosity is a function of temperature. (Lower temperature gives higher viscosity.) Let low-temperature buffer reach operating temperature before starting the run. |
| Microbial growth in buffers. The buffer normally become opalescent due to microbial growth. |
Check buffers, especially those with phosphate, for microbial growth. Replace with fresh buffer if necessary. |
| Sample and collection vessels at different levels. | Adjust the vessels to approximately the same level. |
| The prefilter might be blocked. | Check the prefilter. Preventive action: Prefilters are not meant to substitute sample treatment. |
| Valve not fully open. | Check all valves. Open any that is not fully open. |
Find more causes and remedies in the troubleshooting section.
My column has a gap between the packed bed and adaptor. Can I reuse the column?
| Possible causes | Suggested Remedy |
| Bed support damaged or incorrectly assembled allowing chromatography medium particles to leave the column. | Check the bed support and replace if necessary. Disassemble the column according to instructions. |
| Buffer conditions deviate with regard to temperature, conductivity, viscosity, content of organic solvent (reduces surface tension) or other factor. | Check the buffers and choose more suitable conditions. |
| Increased resistance to flow due to blocked bed support compressing the packed bed. | Clean or change the bed support. Disassemble the column and replace the support according to instructions. Preventive action: Pre-filter or centrifuge sample to avoid residues building up. |
| Poorly packed bed (not sufficiently compressed during packing). (Not applicable for prepacked columns) |
Evaluate the packing using recommended methods. Please be aware of that for small columns, less than 10 ml bed volume, the system dead volume has an impact on the column evaluation values. If the results are poor, refer to the symptom Poor packing evaluation in the troubleshooting section. |
How much sample, in mg or ml of protein can I load onto my column?
Affinity Chromatography
- The binding capacity values listed in the selection guide below, are typical for the given species. However, there might be considerable deviations in binding capacity for different immunoglobulins derivated from same species, even if they are of the same subclass.
- Protein binding capacity is protein-to-protein dependent. The given capacities are to be considered as starting values.
- For optimal separation use approximately one fifth of the total binding capacity
For more information refer to:
Affinity chromatography columns and media selection guide
Glutathione Sepharose selection guide
Ni Sepharose and IMAC Sepharose selection guide
Desalting
- In group separation (desalting) the sample volumes can be up to 30% of the column volume.
- Regarding sample volumes for prepacked columns, please refer to Sample preparation for analysis of proteins, peptides and carbohydrates selection guide.
Gel filtration chromatography
- Choose a sample volume of < 0.5% of the column volume for media with average particle size in the range of 10-15 µm and < 5% of the volume for media with average particle size in the range of 30-100 µm.
- In group separation (desalting) the sample volumes can be up to 30% of the column volume.
- Regarding sample volumes for prepacked columns, please refer to selection guide below:
Sample preparation for analysis of proteins, peptides and carbohydrates selection guide.
Gel filtration columns and media selection guide and product profile selection guide.
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography
- The binding capacity values in the media and column instructions, there are examples and to be considered as starting values. Protein binding capacity is protein-to-protein dependent.
- For optimal separation use approximately one fifth of the total binding capacity.
Ion exchange chromatography
- The binding capacity values in the Ion exchange columns and media product profile, please refer to Ion exchange columns and media product profile selection guide, there are examples and to be considered as starting values. Protein binding capacity is protein-to-protein dependent.
- For optimal separation use approximately one fifth of the total binding capacity.
Reversed phase chromatography
- The binding capacity values in the media and column instructions, please refer to the related document, there are examples and to be considered as starting values. Protein binding capacity is protein-to-protein dependent.
- For optimal separation use approximately one fifth of the total binding capacity.
Can I run two columns in series to increase resolution or capacity?
Gel filtration chromatography
Running columns in series increases the resolution
Affinity chromatography, Hydrophobic interaction, Ion exchange chromatography
Reverse phase chromatography
Running columns in series increases the capacity but may have a bad impact on the resolution
due to increased dead volume.
Please note that back pressure may increase.
My column has run dry. Can I reuse the column?
If the column still is free from bacterial growth it might be possible to reuse the column. It could be worth trying.
Remove the air by running liquid slowly from bottom to top of a vertical placed column at a pressure close to maximum column pressure. The size of air bubbles decreases with increased pressure and facilitate the bubbles escape from the column.
If you don't succeed in removing air from the column, the column must be replaced (prepacked columns) or repacked.
My column contains air, what can I do?
| Possible causes | Suggested Remedy |
| Unclarified lysates may cause increased air bubble formation during purification. | An attached flow restrictor in the chromatography system can prevent this. If a flow restrictor is attached, it is important to change the pressure limit to 0.5 MPa (5 bar9 on the ÄKTAdesign system (where the column and the flow restrictor give a pressure of 0.3 MPa and 0.2 MPa respectively). |
| The column operates at room temperature after having been stored in a cold room. | Allow thermal equilibration before use. |
| - | Reverse the flow direction and pump well degassed water through the column. For recommended volumes and flow rates for your specific column, please refer to media and column instructions. |
More causes and remedies might be presented in the troubleshooting section.
How should I prepare my sample prior to loading the column?
Please prepare the sample according to instructions and handbooks
Prepacked column instructions
Please refer to relevant Instruction.
Other columns
Please refer to relevant Handbook.
What chemicals are compatible with my column?
Please see the chemical stability in the instructions for prepacked columns, empty columns and media.
Accessories
Make sure you have all connectors and tubing needed for running the column.
Place the cursor over any number in the figure to get further information about the components.
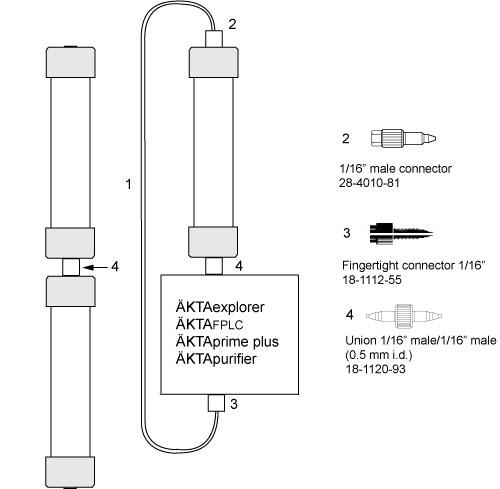
| # | Product Name | Product Code | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tubing cutter, for PEEK, EFTE, and FEP tubing i.d. 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1 and 1.6 mm | 18111246 | 99.55 USD |
Add to cart
|
| 1 | PEEK Tubing, 2 m, i.d. 0.75 mm, o.d. 1/16" | 18111253 | 96.26 USD |
Add to cart
|
| 1 | PEEK Tubing, 2 m, i.d. 0.5 mm, o.d. 1/16" | 18111368 | 73.48 USD |
Add to cart
|
| 1 | PEEK Tubing, 2 m, i.d. 1.0 mm, o.d. 1/16" | 18111583 | 85.34 USD |
Add to cart
|
| 1 | Tubing i.d. 0.25 mm, o.d. 1/16" | 18112095 | 66.24 USD |
Add to cart
|
| 2 | Fingertight connector 1/16" male, narrow | 28401081 | 108.65 USD |
Add to cart
|
| 3 | Fingertight Connector 1/16" Male for Tubing o.d. 1/16" | 18111255 | 123.16 USD |
Add to cart
|
Troubleshooting
Find solutions to product related issues. For unlisted issues please contact local Cytiva service representation.
Worrying peak shape
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Gradient slope or isocratic step too shallow. |
Increase steepness of gradient or isocratic step. |
Poor reproducibility
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Affinity, hydrophobic interaction and ion exchange chromatography - Continuous build-up of contaminants has altered the selectivity of the chromatography medium. |
Clean the chromatography medium according to instructions. |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Column not properly equilibrated |
Check the pH and the conductivity of the effluent before applying the sample. Continue to equilibrate with start buffer if necessary |
Insufficient column regeneration. |
Prolong the regeneration. |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Protein properties change with concentrations |
Dilute or concentrate the sample to minimize effects. |
Proteins precipitate at high concentration. |
Reduce sample concentration and/or binding capacity. |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Column bleeding from previous run. |
Check and adjust your cleaning procedure. |
Column clogged with denatured proteins and/or lipids. |
Clean and regenerate the column and chromatography medium according to instructions. |
Incomplete equilibration of the column. |
Check pH and conductivity of the effluent before applying the sample. Continue to equilibrate if necessary. |
Incorrect pH and/or ionic strength of the solutions. |
Check pH and conductivity and adjust if necessary. Calibrate your conductivity and pH meters. |
Larger sample mass load applied compared with earlier runs. |
Keep mass of sample constant when repeating runs. (High proteins concentration can cause protein interaction, resulting in change of elution profile.) |
Sample volume is different from earlier runs. |
Resolution is dependent on the sample volume. Keep sample volume constant when repeating runs. |
Unusual column appearance
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
The column operates at room temperature after having been stored in a cold room. |
Allow thermal equilibration before use. |
Unsatisfactory elution
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Buffers have wrong pH, ionic strength or solvent concentration. |
Check and adjust the buffer conditions. Calibrate your instruments. |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
For ion exchange chromatography - Ionic strength of the sample too high or pH incorrect |
Check and adjust the ionic strength and/or pH. Calibrate your conductivity and pH meters. |
For ion exchange chromatography - Reduced net charge due to complex between the component in the sample and the target molecule |
Check the composition of the sample. Remove any interfering compounds such as nucleic acids. |
The column not properly equilibrated |
Check the pH and conductivity of the effluent before applying the sample. Continue to equilibrate with start buffer if necessary. |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Column not properly equilibrated. |
Re-equilibrate the column. |
Sample not properly equilibrated. |
Equilibrate sample to correct operating conditions (pH, ionic strength, etc.) |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Column not properly equilibrated. |
Check the pH and conductivity of the effluent before applying the sample. Continue to equilibrate with start buffer if necessary. |
Components in the sample displace the target molecule before elution starts. |
Reduce the concentration of detergent to below it´s critical micelle concentration (CMC) value. |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Target protein not stable under the chosen conditions and partly degrades |
Find better ways to stabilize the protein, e.g. shorten the process time. |
The detergent has formed micelles with the protein, thereby increasing its size and changing its elution position. |
Reduce the concentration of detergent to below it´s critical micelle concentration (CMC) value. |
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Dead volume in chromatography systems is high. |
Minimize dead volume in the chromatography system by decreasing capillary length and dimensions between injector and detector. Bypass unused system components e.g. column valves from the flow path. |
Flow velocity too high. |
Run the separation at a lower flow velocity. This is especially important for adsorbents that bind several substances and where selectivity is low. |
Slop of gradient too steep. |
Use a more shallow gradient. A plateau in the gradient where your protein elutes may improve the resolution. |
Too much sample has been loaded onto the column. |
Decreasing the sample load may improve the resolution significantly. |
Poor product recovery
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Contaminants accumulating in the column. |
1. Optimize the elution conditions |
Back pressure increases during operation
| Possible cause | Suggested remedy |
|---|---|
Auxiliary equipment such as manometers and pumps not working properly. |
Check the function of all auxiliary equipment. Repair/replace if necessary. |
Bent tubing. |
Check that the flow path is not restricted. |
Buffer viscosity too high. |
Check the viscosity of all buffers. Viscosity is a function of temperature. (Lower temperature gives higher viscosity.) Let low-temperature buffer reach operating temperature before starting the run. |
Microbial growth in buffers. |
Check buffers, especially those with phosphate, for microbial growth. Replace with fresh buffer if necessary. |
Sample and collection vessels at different levels. |
Adjust the vessels to approximately the same level. |
The prefilter might be blocked. |
Check the prefilter. |
Valve not fully open. |
Check all valves. Open any that is not fully open. |
