Viruses are extensively used as molecular and cellular biology tools and therapeutic agents. Easy and efficient ways to purify virus particles will aid researchers and accelerate the developments in virology. This application note demonstrates a chromatography method for purification of reovirus RNA virus particles using ÄKTA start, a benchtop chromatography system, and HiTrap Capto Core 700 1 mL column.
Introduction
Viruses are widely studied as pathogens and are extensively used as molecular tools and therapeutic agents. Researchers have found several uses for these unique organisms in medicine and genetic engineering. They have been used in genetic research as tools in gene manipulation and investigation of cellular functions.
Capto Core 700 resin is designed for purification of viruses and other large molecules using mixed mode (multimodal) chromatography. The resin has an inactive outer shell and a ligand-activated inner core. Small molecules like proteins and small nucleotides enter the core and are captured. Viruses and other large particles with a molecular mass greater than Mr 700 000 are excluded and are collected in the column flowthrough.
ÄKTA start, a small benchtop chromatography system, is a handy tool in virus purification along with HiTrap Capto Core 700 column. This application note describes an approach to purification of reovirus, a nonenveloped double-stranded RNA virus using ÄKTA start. This is an efficient, time-saving, laboratory scale virus purification protocol useful for quick and easy screening of virus particles.
Materials and methods
Sample preparation and purification workflow
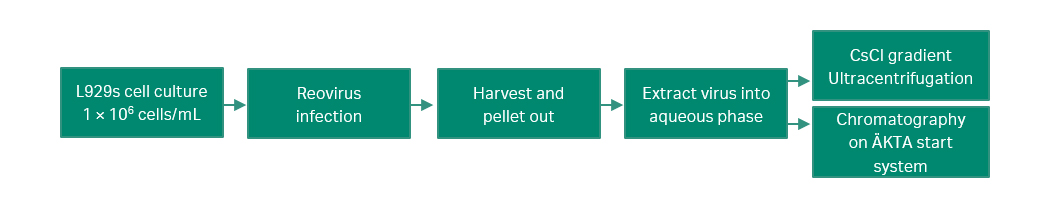
The cell culture, purification protocol, and analysis were originally developed at the Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, University of Alberta according to Figure 1.
HiTrap Capto Core 700 1 mL columns were used for virus purification. The purification protocol was run on ÄKTA start system along with Frac30 fraction collector and UNICORN start control software.
Vivaspin™ ultrafiltration spin columns were used to concentrate the pooled fractions.
Fig 1. Workflow used in the experiment for cell culture of the reovirus, extraction, ultracentrifugation, and purification on ÄKTA start system.
Reovirus purification
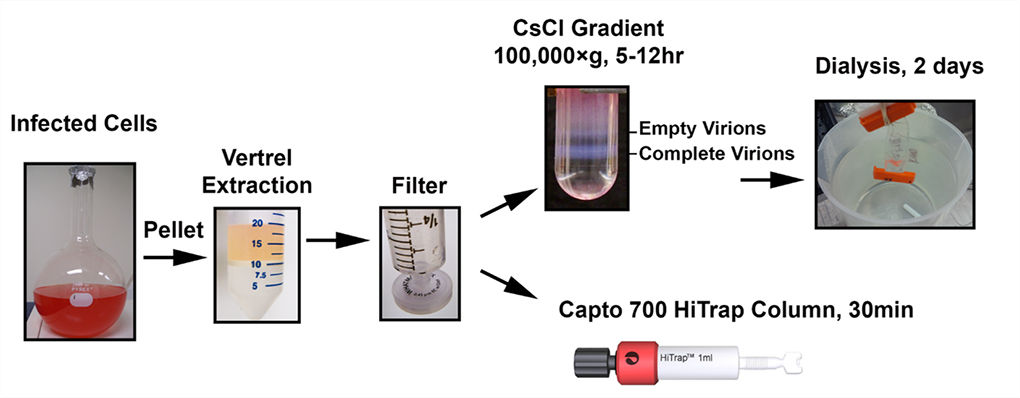
The aqueous phase was passed through a 0.45 μm regenerated cellulose Whatman GD/X filter and divided into two portions. One portion was layered on a 1.2–1.4 g/mL gradient of CsCl, subjected to high-speed ultracentrifugation, and dialyzed against virus stabilization buffer. The second portion was passed through a HiTrap Capto Core 700 column using ÄKTA start chromatography system (Fig 2).
Fig 2. Diagrammatic representation of conventional CsCl density gradient ultracentrifugation and Capto Core 700 chromatography-based reovirus purification strategies. Source, open access article: James, K. et al. Novel high-throughput approach for purification of infectious virions. Sci. rep. 6, article no. 36826 (2016): https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36826
The chromatography method overview is represented in Table 1. Flowthrough fractions were pooled and concentrated using Vivaspin 6 (100 000 molecular weight cutoff, MWCO) sample concentrators and stored at +4°C or aliquoted and stored at –20° C for use over a longer period.
Table 1. Method overview of the chromatographic steps of reovirus purification
| Column | HiTrap Capto Core 700, 1 mL |
| Sample load | 6 mL of clarified cell supernatant |
| Equilibration buffer | Virus dilution buffer: 10 mM Tris, 15 mM MgCl2, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4 |
| Washing buffer | Virus dilution buffer (10 mM Tris, 15 mM MgCl2, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4) |
| Flow rate | 1 mL/min |
| Cleaning in place (CIP) | 30% isopropanol and 1.0 M NaOH |
| Fractionation | Fixed-volume fractionation, 0.5 mL/tube |
| Detection | UV 280 nm |
| System | ÄKTA start, Frac30 Fraction collector, UNICORN start 1.1 |
Purity analysis
Purity of the pooled fractions was analyzed by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Gels were stained with Coomassie™ Blue staining according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Reovirus titers was assessed by standard plaque titration on L929s cells.
Easy, single-step purification of virus particles
Reovirus particles were purified in a single step using ÄKTA start system configured with UNICORN start and Frac30 fraction collector. The core bead design of Capto Core 700 resin significantly removes small contaminating molecules from the sample, allowing easy purification and fractionation of virus particles on Frac30.
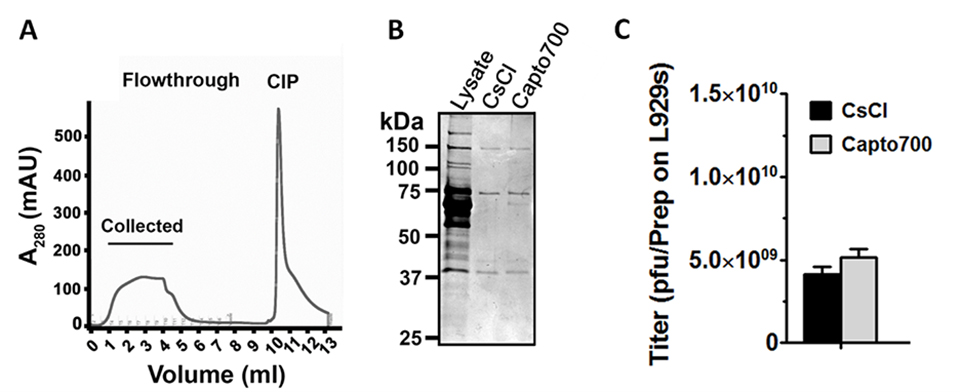
Reovirus particles were collected in the first two to five fractions of the flowthrough, as indicated by a rise in UV at 280 nm in the chromatogram (Fig 3A) and validated by SDS-PAGE (Fig 3B) and standard plaque titration (Fig 3C). Flowthrough fractions were pooled and further concentrated using Vivaspin 6 (100 000 MWCO) sample concentrators.
Fig 3. (A) Chromatographic profile of Capto Core 700 purification of reovirus on ÄKTA start chromatography system. (B) SDS-PAGE profile of the purified reovirus particles with both CsCl density gradient ultracentrifugation and mixed-mode chromatography using Capto Core 700. Gel stained with Coomassie™ blue. (C) Plaque titration assay showing infectivity of reovirus. Source, open access article: James, K. et al. Novel high-throughput approach for purification of infectious virions. Sci. rep. 6, article no. 36826 (2016): https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36826
Purity of Capto Core 700 purified virions equivalent to CsCl gradient
- HiTrap Capto Core 700 column on ÄKTA start system provided highly pure virus particles devoid of contaminating host cell proteins.
- The SDS-PAGE gel provides a visual image of the removal of contaminating host cell proteins. Purity of the virus particles seems comparable to conventional CsCl gradient ultracentrifugation methods. Only dominant structural proteins of reovirus particles (outer capsid σ 3 and μ 1C proteins, and inner capsid σ 2 and λ 1 proteins) are visible in the SDS-PAGE profile (Fig 3B). Therefore, reovirus bands represent whole virus particles rather than soluble virus proteins.
- Both CsCl gradient ultracentrifugation and mixed-mode chromatography using Capto Core 700 provided equivalent reovirus titers as assessed by standard plaque titration on L929s cells (Fig 3). This suggests that when laboratories are not concerned about separating complete virus particles from empty virus particles, chromatography with Capto Core 700 is an effective time saving method to purify reovirus.
Effective removal of immunogenic proteins without affecting virus infectivity
- Purification using Capto Core 700 will provide virus particles free of immunogenic cellular proteins such as cytokines, calreticulin, and HMGB1.
- The study also showed that even after prolonged storage at +4°C, purified reovirus particles retained their infectivity indicating limited proteolysis commonly associated with crude purification procedures.
Conclusions
- Capto Core 700 chromatography on ÄKTA start system equipped with UNICORN start software and Frac30 fraction collector is a straightforward and effective method to purify reovirus.
- This study focuses on reoviruses purification using ÄKTA start system and Capto Core 700 resin. It may be optimized to purify any other virus particles. This rapid virus purification strategy may help researchers using viruses as molecular tools by reducing time and effort needed for virus purification step.
- This method reduces the time and effort spent by researchers on virus purification to a large extent and provides virus particles devoid of contaminating immunogenic proteins.
Acknowledgement
This document is based on the article: James, K. et al. Novel high-throughput approach for purification of infectious virions. Sci. Rep. 6, article no. 36826 (2016) accessible from the following URL: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36826. It has been published under Creative Commons license, CC BY 4.0. Part of the original article has been adapted for this purpose. We acknowledge copyright of the authors and publisher.